General Troubleshooting For DDNS on a TP-Link Wi-Fi Router, LTE Gateway Router, or Deco Router
Archer C5400 , Deco BE65-5G , Archer C5 , Archer C2 , Archer AX95 , Archer AX96 , Deco Voice X50 , Deco E4R , Deco E4S , Deco X4300 Pro , Archer BE850 , Archer C58HP , Deco W6000 , Archer C8 , Archer C9 , Archer C6 , Archer C7 , Archer AX90 , Archer AX55(RU) , Archer AX5400 , Deco X50-PoE , Deco WB10800 , Deco W7200 , Archer AX80 , Archer AX4200 , Archer C3200 , Archer A2 , Archer AX75 , Archer AX73 , Deco PX50 , Deco BE95 , Deco BE65 Pro , Archer A6 , Archer A7 , Archer AX72 , Archer A5 , TL-MR150 , Deco X90 , Archer A8 , Archer A9 , Deco W2400 , Archer AX68 , Deco X95 , Deco X50 Pro , Archer AX5300 , Deco X96 , Deco XM73 , Archer Air R5 , Deco XE75 Pro , Archer AXE300 , Archer AX1500 , Archer BE700 , Archer AX60 , Deco M3W , Archer AX3000 , Deco W3600 , Archer A2600 , Archer AX55 , Deco X50-DSL , Archer AX53 , Deco X68 , Archer AX51 , Archer D50 , TL-MR6400 , Deco X5700 , Archer BE11000 Pro , Archer AX50 , Deco M5 , Deco M4 , Deco HX20 , Deco M3 , Archer AX6000 , Archer C25 , Deco X75 , Archer C24 , DecoX5700 , Deco X50-4G , Archer C21 , Archer C20 , Archer MR200 , Archer MR202 , Archer AX1800 , Deco X50-Outdoor , Deco X73-DSL , Archer BE800 , TL-MR6400(APAC) , Deco X50-5G , Archer BE3600 , Deco X80 , Archer BE7200 , Archer C900 , Archer AX4400 , Archer C50
Recent updates may have expanded access to feature(s) discussed in this FAQ. Visit your product's support page, select the correct hardware version for your device, and check either the Datasheet or the firmware section for the latest improvements added to your product. Please note that product availability varies by region, and certain models may not be available in your region.
DDNS, commonly known as Dynamic DNS, is an automatic method of refreshing a Domain Name Server. DDNS can dynamically update DNS records without the need for direct interaction. It is extremely useful for updating IP address records when the public IP (WAN IP) address changes.
If you run into any issues using the DDNS function on a TP-Link Wi-Fi Router/LTE Gateway Router or Deco Router (henceforth referred to as “Router” in this article), please refer to the following tips to determine whether the issue is due to DDNS or rooted elsewhere in the network.
Tip 1. Will the DDNS domain name remain bound to my Router WAN IP address?
Please note that the DDNS domain name is bound to the true public IP address. If your router's WAN IP address is a private address or CGNAT address, the IP address bound to the DDNS will be different from your Router WAN IP address.
In this scenario, remote access to the router or local server will not function, regardless of whether port forwarding has been properly configured on the Router. This is due to there being at least one additional NAT in front of your router. In this type of scenario, you will need to open related ports on the front-end NAT product(s) as well.
Note: For LTE Gateway Routers in 3G/4G Router mode, SIM cards are used to obtain Internet access. If the WAN IP is not a public IP address, this indicates the front-end NAT is on your ISP’s side. In such cases, you may be unable to open the relevant ports on your front-end NAT device, and may need to contact your ISP to verify whether they can directly assign your network a public IP address.
Tip 2. How to determine whether it is a public IP address
1) Private IPv4 addresses have the following class configurations:
Class A IP addresses: from 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
Class B IP addresses: from 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
Class C IP addresses: from 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
2) Apart from the private IP addresses in the above 3 classes, there is another range of IP addresses. This additional range may appear like a public IP address; however, it is classified as a Carrier Grade NAT (CGNAT) address. CGNAT addresses range from 100.64.0.0 to 100.127.255.255. Typically, these are not true public IP addresses either.
3) Alternatively, you can use a search engine to use known websites that can relay your public IP address information to you on a client device that is connected to the Router, then compare it with the Router’s WAN IP address. If they are the same, the Router’s WAN IP is a true public IP address. If not, this indicates the Router’s WAN IP address is private IP address or a CGNAT address.
Tip 3. How to verify whether my DDNS is functioning properly
Via the nslookup command:
One way to verify if your DDNS is functioning properly is to use the nslookup command via the Command Prompt in Windows. For example, if your DDNS domain name is xxxxx.tplinkdns.com, open a Command Prompt window, then type nslookup xxxxx.tplinkdns.com, and press enter to verify whether the correct IP address can be resolved. If resolves successfully, this means the DDNS is working properly.
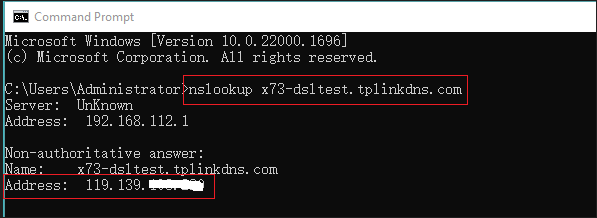
Note: The “correct IP address” being verified is your public IP address. This address may differ from your Router’s WAN IP address, which depends on whether your Router’s WAN IP is a true public IP address.
If you are unable to access the local server remotely via the DDNS domain name, try the following troubleshooting steps:
Step 1. Verify whether your Router’s WAN IP address is a true public IP address.
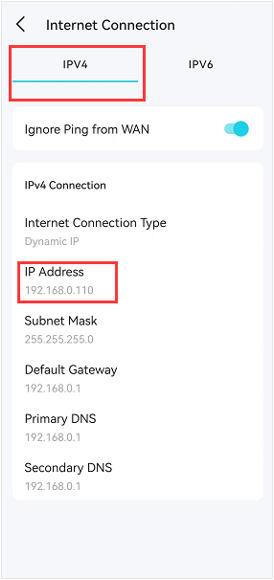
For example, if you have a Deco Mesh Wi-Fi System, you can check the Deco Router WAN IP address within the Deco App under More → Internet Connection → IPv4.
Step 2. Check if the port forwarding rules are configured correctly on the Router for the designated local server.
Note: If you are trying to access the router’s web interface remotely, and not via local servers, please verify whether Remote Web Management is configured correctly on the Router.
Step 3. Verify whether the DDNS is bound to the correct IP address via the nslookup command mentioned in Tip 3 above.
Step 4. Check if you can access the local server via the current public IP address instead of the DDNS. This may confirm whether port forwarding is properly configured and active.
If it is inaccessible remotely via a public IP address, please refer to our Port Forwarding Troubleshooting Guide: Why port forwarding feature is not working on my Wi-Fi router or Deco
Step 5. Contact TP-Link Technical Support and provide us with the following details:
1) Detailed network topology and whether your TP-Link Router WAN IP is a public IP address
2) Screenshots of current port forwarding rules and the DDNS settings page
3) Whether you able to access the local servers remotely via public IP address
Is this faq useful?
Your feedback helps improve this site.
What’s your concern with this article?
- Dissatisfied with product
- Too Complicated
- Confusing Title
- Does not apply to me
- Too Vague
- Other
Thank you
We appreciate your feedback.
Click here to contact TP-Link technical support.
TP-Link Community
Still need help? Search for answers, ask questions, and get help from TP-Link experts and other users around the world.
We have updated our Policies. Read Privacy Policy and Terms of Use here.
This website uses cookies to improve website navigation, analyze online activities and have the best possible user experience on our website. You can object to the use of cookies at any time. You can find more information in our privacy policy .
We have updated our Policies. Read Privacy Policy and Terms of Use here.
This website uses cookies to improve website navigation, analyze online activities and have the best possible user experience on our website. You can object to the use of cookies at any time. You can find more information in our privacy policy .
Basic Cookies
These cookies are necessary for the website to function and cannot be deactivated in your systems.
TP-Link
accepted_local_switcher, tp_privacy_base, tp_privacy_marketing, tp_smb-select-product_scence, tp_smb-select-product_scenceSimple, tp_smb-select-product_userChoice, tp_smb-select-product_userChoiceSimple, tp_smb-select-product_userInfo, tp_smb-select-product_userInfoSimple, tp_top-banner, tp_popup-bottom, tp_popup-center, tp_popup-right-middle, tp_popup-right-bottom, tp_productCategoryType
Livechat
__livechat, __lc2_cid, __lc2_cst, __lc_cid, __lc_cst, CASID
Youtube
id, VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE, LOGIN_INFO, SIDCC, SAPISID, APISID, SSID, SID, YSC, __Secure-1PSID, __Secure-1PAPISID, __Secure-1PSIDCC, __Secure-3PSID, __Secure-3PAPISID, __Secure-3PSIDCC, 1P_JAR, AEC, NID, OTZ
Analysis and Marketing Cookies
Analysis cookies enable us to analyze your activities on our website in order to improve and adapt the functionality of our website.
The marketing cookies can be set through our website by our advertising partners in order to create a profile of your interests and to show you relevant advertisements on other websites.
Google Analytics & Google Tag Manager
_gid, _ga_<container-id>, _ga, _gat_gtag_<container-id>
Google Ads & DoubleClick
test_cookie, _gcl_au
Meta Pixel
_fbp
Crazy Egg
cebsp_, _ce.s, _ce.clock_data, _ce.clock_event, cebs
lidc, AnalyticsSyncHistory, UserMatchHistory, bcookie, li_sugr, ln_or


