What can I do if my client can’t roam between my wireless router and TP-Link AP & Range Extender product?
TL-WPA271KIT , TL-WPA4220 , RE400 , TL-WPA7519 KIT , TL-WA801ND , TL-WPA8730 KIT , RE505X , RE715X , TL-WPA4220KIT , TL-WPA7510 KIT , TL-WPA4226 KIT , TL-WA701ND , TL-WPA7617 , TL-WPA7617 KIT , TL-WPA4226T KIT , RE650 , RE450 , RE603X , TL-WA750RE , RE355 , TL-WPA7619 KIT , RE700X , TL-WPA4220 KIT , RE1500X , TL-WPA8635P KIT , RE1750X , RE780X , TL-WA901ND , TL-WA850RE , TL-WPA4235P KIT , TL-WPA9610 KIT , TL-WPA281KIT , TL-WPA271 , TL-WA854RE , TL-WPA4221 KIT , RE500 , RE600X , TL-WPA281 , TL-WPA8630 KIT , RE705X , TL-WPA2220 , RE605X , TL-WPA4227KIT , RE500X , TL-WPA1300P KIT , RE580X , TL-WA730RE , TL-WPA2220KIT , TL-WPA4530 KIT , TL-WPA8631P KIT , TL-WPA7817 KIT , RE2700X , RE580D , TL-WPA4225 KIT , TL-WA830RE , TL-WPA7517 KIT
Recent updates may have expanded access to feature(s) discussed in this FAQ. Visit your product's support page, select the correct hardware version for your device and check either the Datasheet or the firmware section for the latest improvements added to your product.
Problem Description:
You may have bought some AP products like TL-WA801ND or some RE products like TL-WA850RE, and you used this product to extend your wireless network.
But when you are walking between your main router and your AP (they have the same wireless name and password), you may find that your wireless client like a mobile phone is still sticking to the distant device and will not roam to the nearest device.
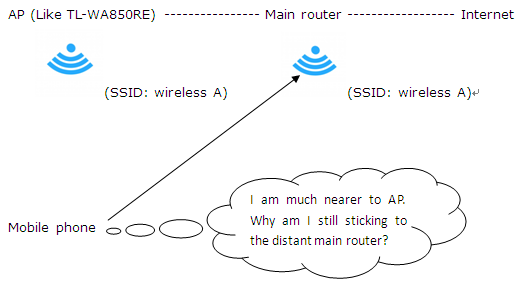
How roaming works:
Roaming is purely a client decision. The wireless client is responsible for deciding it needs to roam, and then detecting, evaluating, and roaming to an alternative AP. WLAN standards bodies (such as IEEE) and industry bodies (such as Wi-Fi Alliance) do not specify when a client should roam, or how the client roams.
So roaming or not roaming, it is totally decided by your wireless client’s roaming algorithm. Different wireless client vendors’ roaming algorithms are also different and are not generally published.
Resolution:
There is no role played by TP-Link AP and RE products in this client roaming process. So we suggest you should configure your wireless client to achieve fast roaming. Please follow the steps below to configure your wireless client.
Precondition:
You need to configure the root wireless router and range extender or AP with the same wireless name (SSID) and same wireless password & authorization method.
1) For laptop:
Some WNIC vendor does give some mechanism to control this roaming behavior. Note: The brands like Intel and Ralink I will introduce are the wireless network adapter vendors.
1 In Intel, it is known as roaming aggressiveness and this setting allows you to define how aggressively your Wi-Fi client roams to improve wireless connection.
Here are the configuration methods on Intel WNIC:
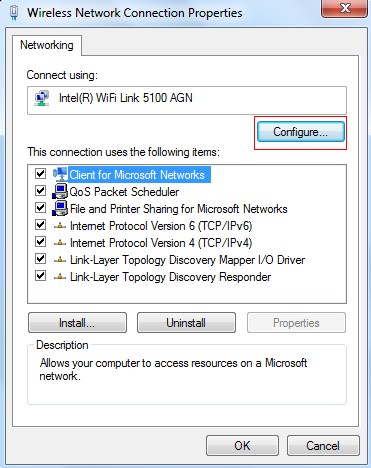
You can go to control panel -> network and internet -> network connection and choose the wireless connection. Right click the wireless connection and choose properties, you will see the following picture on the left.
Click configure and you will see the following picture on the right. Choose Advanced and choose roaming aggressiveness.
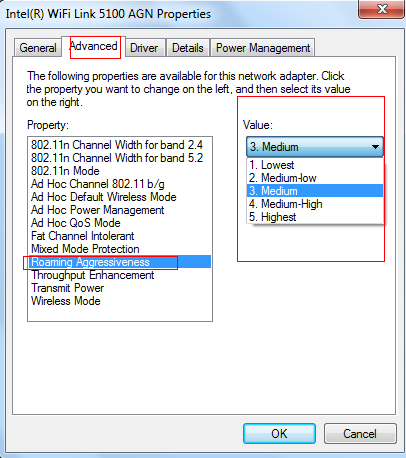
You can see there are 5 options. Here are the explanations of these five options:
l Lowest: Your wireless client will not roam. Only significant link quality degradation causes it to roam to another access point.
l Medium-Low/Medium-High: Allow Roaming.
l Medium: Balanced setting between not roaming and performance.
l Highest: Your Wi-Fi client continuously tracks the link quality. If any degradation occurs, it tries to find and roam to a better access point.
2 In Ralink, there are similar settings just like Intel except Ralink uses the name roaming sensitivity instead of roaming aggressiveness:
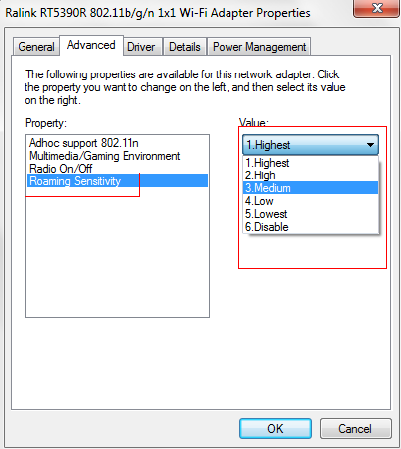
3 So if you want that your laptop can roam to a nearer AP swiftly and aggressively, you can set roaming aggressiveness or roaming sensitivity as Highest. This method is also suitable for other vendor’s WNIC except the name other vendors used may be different.
2) For mobile phone:
Unfortunately for now, there is hardly method to control the mobile phone’s roaming behavior.
1. Blackberry mobile phone:
We only know that blackberry’s mobile phone can control its own roaming process. This is the link for blackberry mobile phone:
http://docs.blackberry.com/en/admin/deliverables/7229/WLAN_Roaming_Thresholdc_607199_11.jsp
So if you have a blackberry phone, you can set Wi-Fi Roaming Threshold as high, then your BlackBerry device roams aggressively to access points with better signal strength.
2. Other mobile phones:
For now, we don’t know if there are any other mobile phones which have the settings to control its roaming behavior just like blackberry phone.
Before the mobile phone manufacturers improve their products’ roaming performance, we can use some third-party software to achieve fast roaming. For example, some android APPs like wifi roaming fix. Here is the official link of this software: http://www.heleron.com/ . You can install this APP from Google play too.
There are also many other different APPs for each mobile phone system. You can get it from APP market.
Here are the screenshots of the ”wifi roaming fix” .
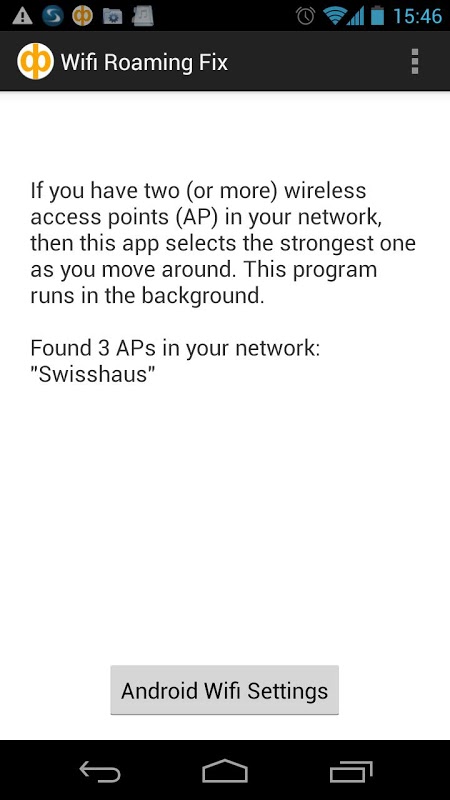
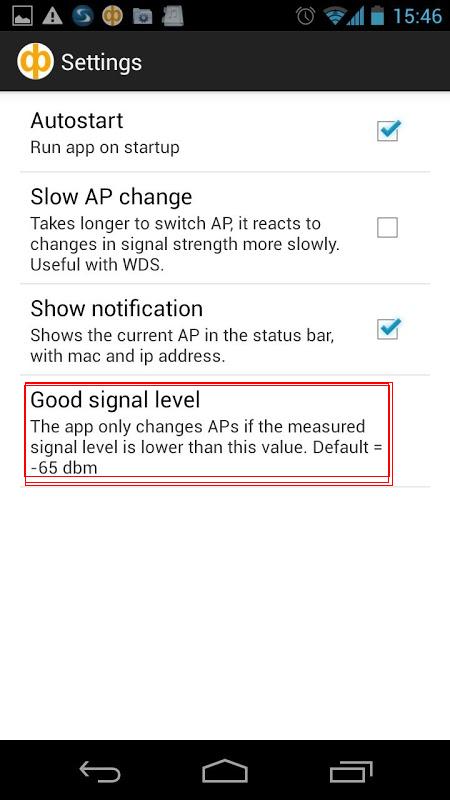
You can choose settings and choose good signal level to set the sensitivity of your phone’s roaming behavior. The bigger number you choose, the more aggressive your phone’s roaming will become (-35dBm is the biggest number). We suggest you should choose -45dBm or -50dBm as good signal level.
If you set good signal level too big, your mobile phone may roam frequently. This may interfere with your Internet surfing.
At last, if all the solutions can’t solve the problem you faced. You can contact your client’s manufacturer for help as roaming process is totally decided by the client itself.
Looking for More
Questa faq è utile?
Your feedback helps improve this site.
What’s your concern with this article?
- Dissatisfied with product
- Too Complicated
- Confusing Title
- Does not apply to me
- Too Vague
- Other
Grazie
We appreciate your feedback.
Click here to contact TP-Link technical support.
Questo sito utilizza i cookies per migliorare l'esperienza di navigazione, analizzare le attività online e offrire agli utenti una migliore user experience. Puoi disattivare o rifiutare il loro utilizzo in qualunque momento. Per maggiori informazioni consulta la nostra privacy policy .
Questo sito utilizza i cookies per migliorare l'esperienza di navigazione, analizzare le attività online e offrire agli utenti una migliore user experience. Puoi disattivare o rifiutare il loro utilizzo in qualunque momento. Per maggiori informazioni consulta la nostra privacy policy .
Basic Cookies
Questi cookies sono necessari per il corretto funzionamento del sito e non possono essere disattivati nel tuo sistema.
TP-Link
accepted_local_switcher, tp_privacy_base, tp_privacy_marketing, tp_smb-select-product_scence, tp_smb-select-product_scenceSimple, tp_smb-select-product_userChoice, tp_smb-select-product_userChoiceSimple, tp_smb-select-product_userInfo, tp_smb-select-product_userInfoSimple, tp_top-banner, tp_popup-bottom, tp_popup-center, tp_popup-right-middle, tp_popup-right-bottom, tp_productCategoryType
Livechat
__livechat, __lc2_cid, __lc2_cst, __lc_cid, __lc_cst, CASID
Youtube
id, VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE, LOGIN_INFO, SIDCC, SAPISID, APISID, SSID, SID, YSC, __Secure-1PSID, __Secure-1PAPISID, __Secure-1PSIDCC, __Secure-3PSID, __Secure-3PAPISID, __Secure-3PSIDCC, 1P_JAR, AEC, NID, OTZ
Analytics e Marketing Cookies
I cookies analitici ci permettono di analizzare le tue attività sul nostro sito allo scopo di migliorarne le funzionalità.
I marketing cookies possono essere impostati sul nostro sito dai nostri partner pubblicitari allo scopo di creare un profilo di tuo interesse e proporti contenuti pubblicitari rilevanti su altri siti.
Google Analytics & Google Tag Manager
_gid, _ga_<container-id>, _ga, _gat_gtag_<container-id>
Google Ads & DoubleClick
test_cookie, _gcl_au
Meta Pixel
_fbp
Crazy Egg
cebsp_, _ce.s, _ce.clock_data, _ce.clock_event, cebs
lidc, AnalyticsSyncHistory, UserMatchHistory, bcookie, li_sugr, ln_or


